Everstate is an ideal-type for our very real countries created to foresee the future of the modern nation-state. In the case of this specific scenario-building, we are setting the stage for Everstate, by attributing values to key influencing variable to be able to develop the scenarios. The explanations regarding the methodology used to develop the narrative is explained in “Constructing a foresight scenario’s narrative with Ego Networks.”
Geopolitical situation: Everstate, a middle-range power
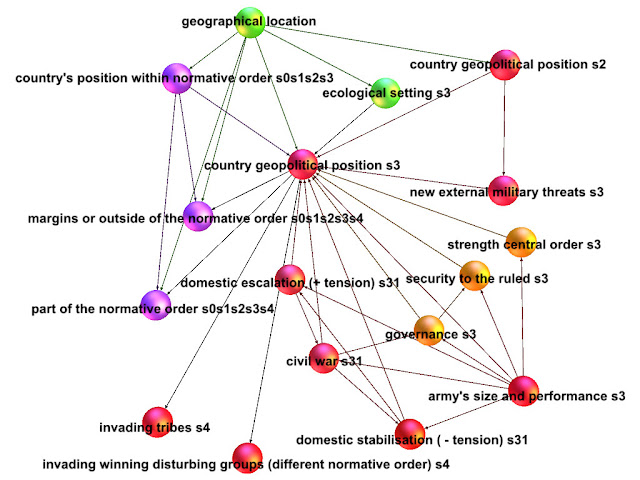
As a medium state power located on the Eurasian land mass, Everstate had not seen its geopolitical position fundamentally altered since the end of the Cold War, and even since the end of World War II. However, recently, some tensions had begun building up and Everstate had to start contending with them as they could easily transform in very concrete new external military threats.
What had contributed to maintain its geopolitical position were different factors. The impact its ecological setting could have had on its geopolitical position was remote and long forgotten. Yet, it could still play a part. Similarly, the various actors of Everstate did not perceive anymore its continental climate, soften for the southeastern part of the country by the influence coming from the sea, as a factor influencing geopolitics. The harshness of the snowy and mountainous North had long been perceived as a bounty for tourism. The large river crossing the country from Northwest to Southeast was seen from the perspective of industry, trade and tourism and no longer as a possible way in for invaders. Finally, it had been centuries since the rich agricultural eastern plain had not attracted invaders or greedy neighbours looking for rich lands.
Everstate’s army was efficient, considering current military techniques, expertise and previous experience, even if its size had been reduced. The previous period of peace, as well as the evolution of society and the size of the population had led to this downsizing. The defence forces could thus carry out with success very specific and targeted missions, but not deploy extensively and exhaustively.
In Everstate, central order was relatively strong. The governance was quite efficient although some areas were starting to be less effectual. As a result, evidence of discontent, so far apparently limited to complaining and grumbling, had started being recorded, letting believe that the security of citizens was not anymore fully ensured. We were, however, apparently quite far from major domestic escalation of violence, and even further from civil war, which both could impact the geopolitical situation. Furthermore, as none of the latter events had occurred for the last century or so, they were deemed to be impossible: people were thought, rightly or not, to have become unable of such actions, because of the comfortable life they had enjoyed for so long.
At the beginning of this second decade of the 21st century EVT, Everstate was well in line with the most common winning international norms. This gave the country international legitimacy and implied that it did not have to face any major normative war against the dominant order. Its society was modern; it believed in material well-being, constant improvement thereof and in the virtues of constant and rising economic growth; it obeyed the law of the market and of capitalism, economics being quite foremost.
Meanwhile, the old monotheist religions still existed but their institutional and political role was marginal, as most of society was mainly concerned with other matters, more materialistic than spiritual. Nevertheless, as in other countries, some tensions existed between small groups of one or the other monotheist religion and sometimes flared up.
Everstate’s governance starts displaying a creeping loss of performance
Governance was thence still quite efficient, with, nevertheless, a slow, creeping loss of performance.
The state was organised according to a formal and rational-legal bureaucracy, upheld by a legal apparatus. It was subdivided administratively according to both geography and major domains of interest (defence, foreign affairs, homeland security, agriculture, trade and industry, tourism, finance, etc.) related to the security of Everstate, as identified throughout the previous ruling periods.
Everstate was governed under a democratic parliamentary regime. As a result, Parliament was involved in political decision-making, would it be only through the restraining power it exerted over the Executive. The political game that was played within Everstate’s ruling elite was classical. It involved obviously the search for power of the nation’s elected representative. Yet, another power struggle, unseen and forgotten was also at play: the nation, this imagined body of citizens (Anderson, 1991), also tried protect its power.
As part of the international society and obeying its norms, Everstate was a full member of the various international institutions that upheld those norms, from the United Nations, to the organisations of the Washington Consensus (IMF, World Bank) and to the World Trade Organization (WTO) (Watson, 1992).
Everstate, as many other states in the world, was also a member of a regional institution, a Regional Union of independent and sovereign democratic states, it had joined freely in the decades following World War II. The Regional Union is neither a Federation, as the United States, Canada, India or Germany, for example, nor a Confederation, but something different, in the making. Its mission, shape, organisation, membership, areas of exclusive or only shared competence and consultative responsibility are being continually reworked and redesigned through various treaties and pacts. It adds one more layer of complexity to the overall governance of Everstate.
In Everstate, the power of the ruler (the nation and its representatives) was neither weak nor strong. However, as, by comparison, the power of various elite groups was relatively strong, then, some appropriation of public power was taking place. Because the separation between the public and private domains had been achieved for some time, this appropriation of public power was either hidden as rampant corruption and nepotism, or taking new forms that were still difficult to unmask and name. The appropriation of public power by these elite groups had direct consequences on governance. Indeed, it lowered its efficiency and perverted its objectives.
The nation-state’s income had been slowly but steadily growing over the past decades. However, it had to be seen in the light of the necessary expenses that seemed to grow uncontrollably faster.
Indeed, as society had lived at peace and developed over the last 60 years, it had grown more complex. Conditions had changed, from the way to live and relate to each other with urbanization and digital and communication technology, to food availability and quality, to health behaviour. Meanwhile new threats had emerged. This led to a more complex situation in terms of governance. While governing implied more tasks and more complex ones, it became more costly. Hence, a few decades ago, the various resources extracted for governance and for ensuring the security of the citizens had started to be insufficient. This phenomenon was accentuated by the appropriation of public good and power by elite groups.
The legitimate monopoly of violence of the state was still there. Nonetheless, it was nevertheless weakening, as the reduction of overall available resources had started taking their toll. Even if such events were thought to be improbable by most, any evolution involving rising grievances up until an escalation towards civil war would be affected by this weakening monopoly of violence. In turn, if such an unlikely and unfortunate spiral started, it would further impact the army’s performance, the monopoly of violence and governance.
The legitimacy of Evertstate’s political system, inherited from past dynamics, was still strong and its impact was thus positive. As a result, despite a security to the ruled – or the citizens – that was starting to be less than perfect, no risk of strong rising discontent and polarisation was thought to be possible.
Notes and References
The first version of this article was published on 2 January 2012.
* We do not here detail the nodes (variables) containing s4. Indeed s4 concerns the future and will be developed later on.
Anderson, Benedict, Imagined communities: reflections on the origin and spread of nationalism, (New York: Verso 1991).
Ertman, Thomas, Birth of the Leviathan: Building States and Regimes in Medieval and Early Modern Europe, (Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1997).
Taylor, Robert The State in Burma, (London: Christopher Hurst, 1987) – notably for the separation between public and private domain, see p.66.
Watson, Adam, The Evolution of International Society: a Comparative Analysis, (London: Routledge, 1992).
Zellman, Ariel, “Birth of the Leviathan by Thomas Ertman” Blog post.